Understanding Modern Threats and Essential Security Controls
The Data Security Battlefield.
Your company's most valuable asset isn't on your balance sheet. It's the data you collect, analyze, and store every single day. In an era where a single click can trigger a million-dollar breach, protecting that asset is no longer an IT issue; it's a core business survival skill.
Understanding Data Security Fundamentals
Data security represents the critical practice of safeguarding organizational data against risks and threats. This field organizes protection efforts around three core dimensions: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, forming what's commonly known as the CIA Triad in information security.
The CIA Triad Explained
Confidentiality focuses on preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data, whether from internal or external sources.
Organizations implement multiple security layers to maintain confidentiality, including network perimeter defenses, role-based access control (RBAC) systems, comprehensive data encryption, and multi-factor authentication protocols.

Integrity ensures data remains accurate and unaltered, protecting against unwanted modification or deletion. These threats can stem from accidental incidents, natural disasters, or malicious attacks aimed at disrupting operations.
Key integrity protection measures include digital signatures and encryption technologies that verify data authenticity and prevent tampering.
Availability guarantees that authorized users can reliably access data when needed. IT operations teams bear primary responsibility for maintaining availability through robust infrastructure management, proactive monitoring, and rapid recovery systems that minimize downtime during failures.
Distinguishing Between Data Security, Protection, and Privacy

While often used interchangeably, these terms represent distinct aspects of data management:
Data Security protects against unauthorized access and misuse that could lead to data leakage, corruption, or destruction. Example: Using encryption to safeguard data even if systems are compromised.
Data Protection focuses on backup and recovery strategies to prevent data loss. Example: Maintaining regular backups to restore data following cyberattacks or system failures.
Data Privacy concerns proper data handling according to sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and user consent. Example: Isolating personally identifiable information (PII) in secure, specialized databases.
Modern Data Security Threats
Today's digital landscape is a minefield of sophisticated threats that target your most valuable asset: data.
Beyond simple viruses, organizations now face targeted social engineering schemes that trick employees, stealthy advanced persistent threats that lurk undetected for months, and the ever-present danger of ransomware that can hold entire operations hostage.

Complicating this are internal vulnerabilities like shadow IT and security misconfigurations, creating attack surfaces that many companies don't even know they have.
Attackers increasingly use manipulation techniques to gain data access, with phishing representing the most common approach. These attacks use deceptive messages appearing to originate from trusted sources, tricking employees into revealing credentials, clicking on malicious links, or opening infected attachments that compromise organizational networks.
Security Misconfiguration
Systems with improperly defined security settings or default credentials create significant vulnerabilities. Misconfigured applications, servers, or workstations, whether in cloud or on-premises environments, can lead to massive data breaches, resulting in business disruption, reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and legal consequences.
I'd like to remind Canadians that Pierre Poilievre still hasn't updated his security clearance because why would he choose to be an accountable and accurate "leader" when it's so much easier to spout misinformation for rage bait.
— Patrick Gagnon (@patgagnon_75)
12:02 PM • Oct 7, 2025
Shadow IT
The unauthorized use of third-party applications and services creates blind spots in security strategies. Employees often turn to familiar personal tools that seem more efficient than company-approved alternatives, potentially exposing sensitive data to insecure platforms and creating compliance violations.
Ransomware
This escalating threat uses malware to encrypt files and systems, demanding payment for restoration. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has democratized access to sophisticated attack tools, while double extortion techniques both encrypt data and threaten public exposure. Infection vectors include email attachments, compromised software, vulnerable applications, and infected websites.

Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
These sophisticated, long-term network attacks focus on stealthy data monitoring and extraction rather than immediate system compromise. APT attackers typically target high-value organizations like major corporations and government institutions to steal strategic information over extended periods.
Essential Data Security Controls
To defend against evolving threats, organizations must implement a layered defense of essential security controls.
This foundation includes robust access management to ensure only authorized users reach sensitive data, comprehensive encryption to protect information both at rest and in transit, and reliable backup systems for rapid recovery when breaches occur.
The Cyber attack on #Mtiba wil have a very huge impact on Data Privacy Compliance for Organizations beyond hiring legal officers to do DP Policies. Information Managers have a huge task. from ICT to Records Personnel, The Country needs you. Do your part #DataPrivacy#CyberAttacks
— 27th Don (@DonVictorSimon)
10:42 AM • Oct 29, 2025
Together, these controls create a resilient security posture that protects data confidentiality, integrity, and availability across your organization.
Access Controls
Implement physical and digital mechanisms that restrict entry to critical systems and data. This includes mandatory authentication for all devices, networks, and applications, coupled with physical security measures for sensitive locations.
Authentication
Deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems that require multiple verification methods, combining knowledge factors (passwords), possession factors (mobile devices), and inherent factors (biometrics), to significantly enhance identity verification.
Backup and Recovery
Maintain regular, secure backups disconnected from primary networks as a fundamental defense against data loss from disasters, system failures, or ransomware attacks. Modern backup strategies should include frequent testing and rapid restoration capabilities.

Data Erasure
Establish systematic processes for removing redundant, duplicate, or unnecessary sensitive data. Use proper data destruction techniques that completely erase storage devices, as standard deletion methods often leave data recoverable by attackers.
Data Masking
Implement anonymization and randomization techniques that hide sensitive information while maintaining data utility for authorized purposes. Modern database systems include built-in masking capabilities that can selectively protect sensitive fields while displaying non-sensitive data normally.
Data Resiliency
Design systems with failure resistance and rapid recovery capabilities. Cloud-based storage solutions provide powerful replication features that distribute data across multiple geographical locations, ensuring continuous availability even during major infrastructure failures.
However, true resilience requires more than just data replication; it demands intelligent data awareness.
This is where DataManagement.AI transforms your storage into a "Context Cloud," providing a unified governance layer that understands not just where your data is stored, but what it contains, how it's used, and who should access it.

Our platform ensures that during a failure, your recovery isn't just fast, it's context-aware, automatically maintaining security policies, compliance controls, and data relationships across your entire ecosystem.
Encryption
Apply robust encryption to data both at rest and in transit, as required by most regulatory standards. Effective encryption strategies must include careful key management practices to prevent unauthorized access to decryption capabilities.
Data Security Solutions
Modern data security challenges require equally modern solutions. Today's organizations leverage specialized tools that automate critical protection tasks, from data discovery platforms that automatically locate and classify sensitive information across your entire digital estate, to integrity monitoring systems that detect anomalous access in real-time.
These solutions provide the visibility and automated enforcement needed to manage data security at scale, ensuring compliance and significantly reducing the attack surface.
Data Discovery and Classification Tools
Automated scanning tools map organizational data across structured and unstructured repositories, including file systems, databases, and cloud storage, identifying sensitive information and vulnerabilities while providing the foundation for targeted protection strategies.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) is a process used for investigating your data to discover patterns, anomalies, relationships, or trends using statistical summaries and visual methods.
Let's find out more 🧵👇
— David Andrés 🤖📈🐍 (@daansan_ml)
9:00 AM • Nov 25, 2023
Data and File Integrity Monitoring
These solutions provide comprehensive visibility into data access patterns, detecting anomalous behavior, generating alerts for suspicious activity, and maintaining detailed audit trails for compliance and investigation purposes.
Vulnerability Management Tools
Specialized scanners identify security weaknesses across IT environments, detecting outdated software, misconfigurations, weak credentials, and database-specific vulnerabilities like code injection points.

Automated Compliance Management
Purpose-built tools incorporate regulatory requirements to automatically assess compliance status, identify issues, and generate audit reports, significantly reducing manual effort while improving accuracy.
To operationalize this efficiency and move from automated compliance to intelligent data governance, you need a platform built for the task.
DataManagement.AI delivers exactly that. It leverages AI to not only ensure compliance but to proactively manage, classify, and secure your entire data landscape, turning governance from a cost center into a strategic advantage.

Discover how to automate your compliance and unlock the intelligence within your data.
Data Security Best Practices
Effective data security extends beyond technology to encompass people and processes. Foundational practices include maintaining comprehensive data classification systems, enforcing the principle of least privilege through robust identity management, and fostering a culture of security awareness through continuous employee training.
These strategic approaches create a human-centric defense layer that complements technical controls, ensuring your entire organization operates as a unified front against data threats.
Identify and Classify Sensitive Data
Collaborate with security teams to systematically catalog and categorize data based on sensitivity, compliance requirements, and organizational value. Maintain strict controls over classification changes, permitting modifications only by authorized personnel.
What's the most critical first step in building a strong data security posture?Where should companies start with data security? |
Develop Unified Data Security Policies
Create comprehensive data inventories encompassing all storage locations and formats. Address unmanaged areas like personal devices and shadow IT services through clear policies and monitoring. Implement consistent protection measures and alerting systems for sensitive data across the organization.
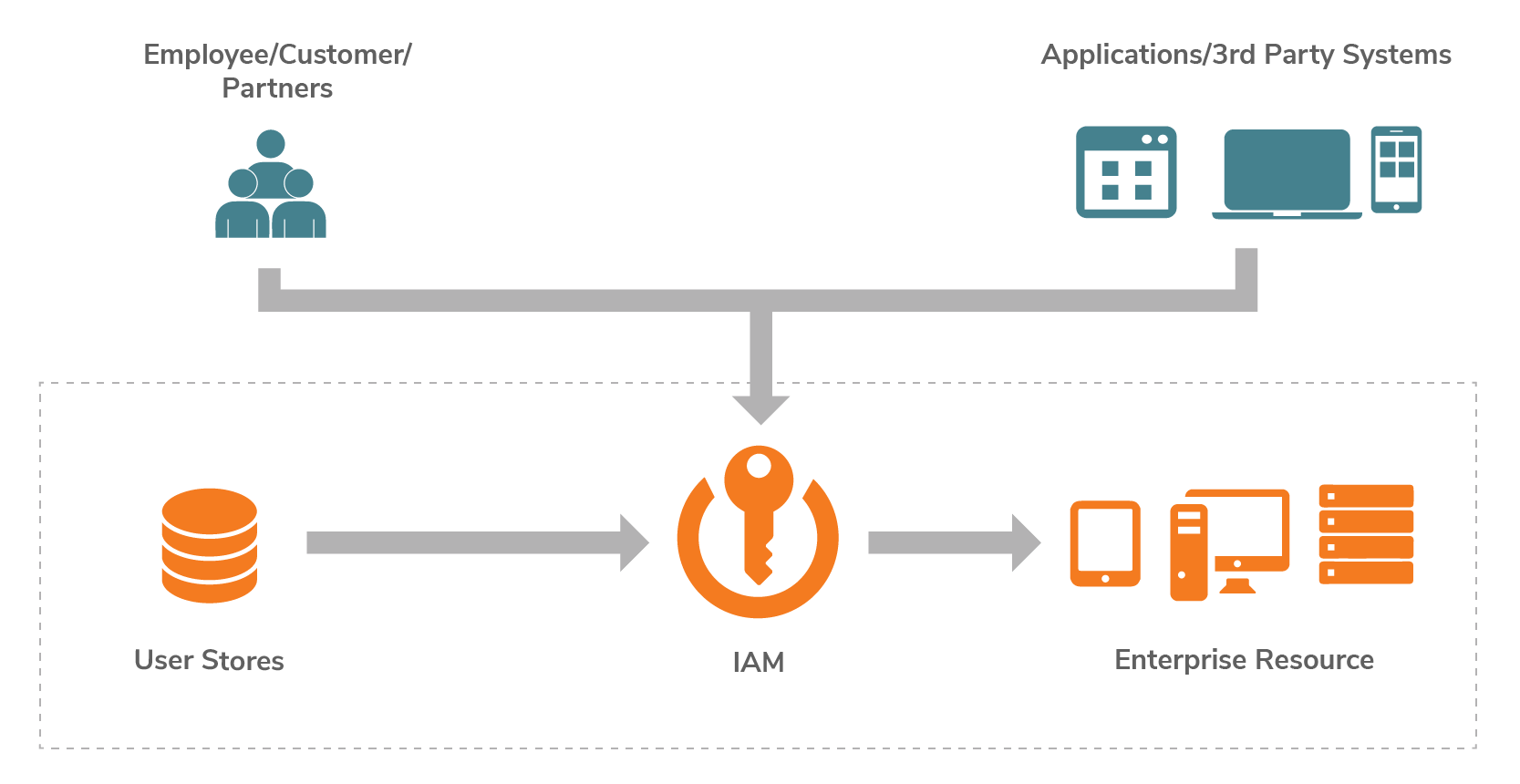
Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Deploy IAM solutions enforcing least-privilege access through role-based permissions. Utilize multi-factor authentication to mitigate credential compromise risks. Modern IAM platforms support hybrid environments, enabling consistent policy enforcement across on-premises and cloud infrastructures.
Conduct Ongoing Employee Security Training
Develop comprehensive training programs that explain security policies, demonstrate proper data handling procedures, and teach threat recognition skills. Focus on practical guidance, including strong password practices, phishing identification, and secure device management. Maintain regular training updates to address evolving threats and reinforce security awareness.
The Private Equity Challenge: Data Security as a Value Driver
For private equity firms, robust data security is no longer just a technical checklist item; it's a critical component of valuation and risk management. During due diligence, a portfolio company's data security posture directly impacts both its purchase price and long-term viability.

Firms now scrutinize data governance frameworks and compliance postures with the same intensity as financial statements, recognizing that undiscovered vulnerabilities or post-acquisition breaches can devastate multiple expansion and exit timelines.
Implementing strong data security controls isn't merely protective; it actively enhances enterprise value by building buyer confidence, ensuring operational continuity, and creating a defensible competitive moat that survives even the most rigorous acquisition scrutiny.
Strategic Implementation Approach
Successful data security requires coordinated effort across technology, processes, and people. Begin with a thorough data assessment and classification, then implement appropriate controls based on risk prioritization.
Maintain continuous monitoring and regular policy reviews to adapt to changing threat landscapes and business requirements.
Remember that data security represents an ongoing process rather than a one-time project.
Organizations must foster a culture of security awareness, maintain vigilance against emerging threats, and continuously refine their protection strategies to safeguard valuable data assets effectively.
By understanding these fundamental principles and implementing comprehensive protection measures, organizations can build robust data security postures that support business objectives while mitigating risks in an increasingly complex threat environment.
Turning these principles into a consistent, automated practice is the greatest challenge. DataManagement.AI is the partner that empowers this evolution.

Our platform acts as your always-on central nervous system for data security, using AI to maintain constant vigilance, automate threat detection, and continuously refine data protection policies across your entire estate.
It transforms your security posture from a manual checklist into a dynamic, self-improving asset. Move from understanding principles to implementing intelligent, automated protection.
Warm regards,
Shen and Team
Social Engineering Attacks